How Long Does it Take to Adjust to New Hearing Aids?
When you first get hearing aids, one of the biggest questions on your mind


When you first get hearing aids, one of the biggest questions on your mind
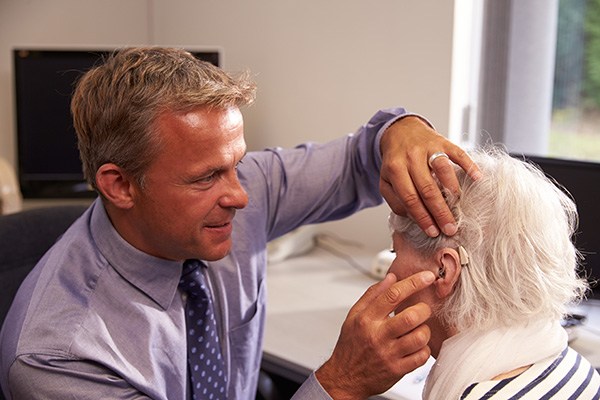
Choosing the right hearing aid isn’t just about finding something

When a child has hearing loss, it affects far more than just their ability